The Analytics with Python Workflow contains an end-to-end workflow for large-scale predictive analysis in tweet engagement prediction. It is originated from intel's democratization solution for the ACM RecSys-2021 challenge and is designed to be generalizable for a wide range of binary classification tasks on large-scale tabular dataset. The top 3 features of this workflow includes
- distributed data preprocessing, XGBoost training and hyperparameter optimization
- rich data processing & feature engineering techniques for large and heterogeneous input data (from 20 original features to 262 training features)
- simple but effective training strategies on CPU, e.g. training set subsampling, model stacking
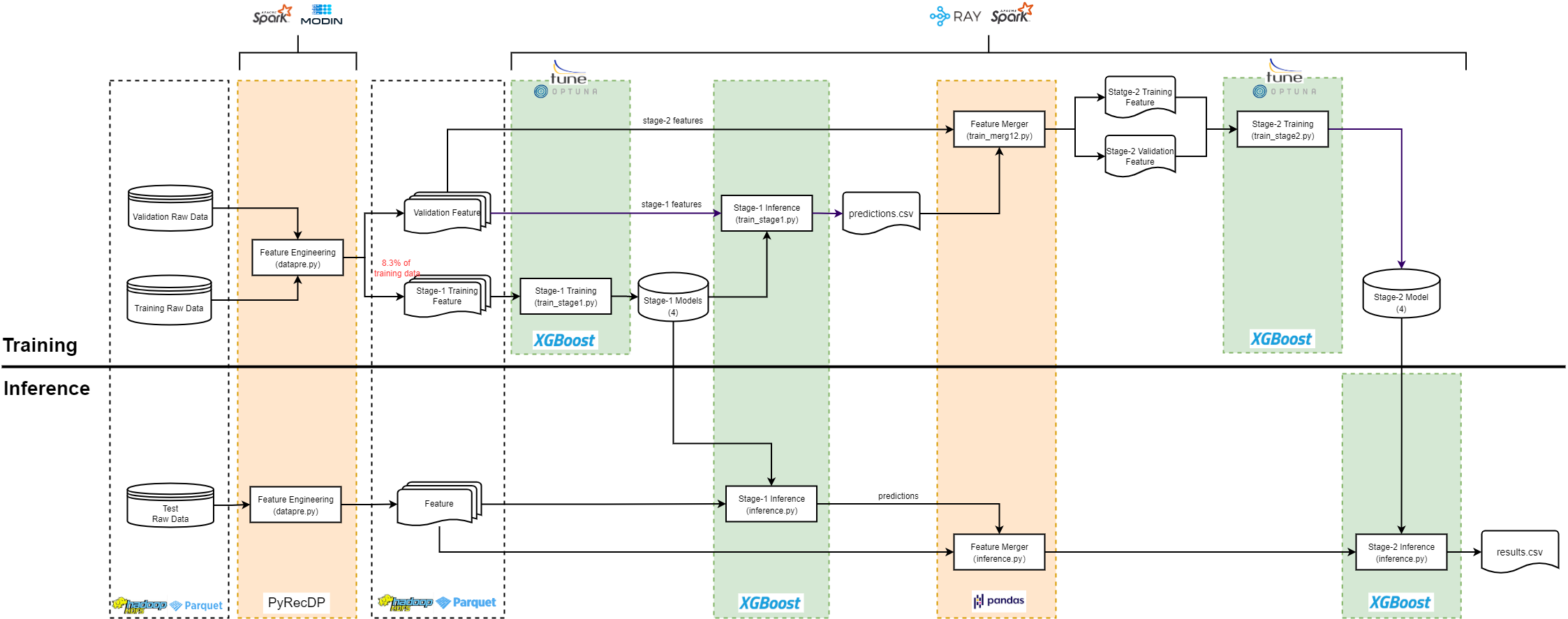
- As with all machine learning tasks, there are 2 phases in the T4 workflow: Training and Inference. we use 2-stage model stacking for training. Stacking is an ensemble method, in which we train new models that uses the prediction of other models as an input.
- As shown in the diagram, stage-1 models are trained using the stage-1 training features and then used to make predictions on the validation features. Next, these predictions are merged into the validation features and used as additional features for stage-2 training. We also split the original validation features into 2 part: one for training and one for validation. The final training results are evaluated on the stage-2 validation features.
- we use training set subsample for training, where only 8.3% of the original training set is used for training
- we include 2 ecosystems in one workflow. The workflow is designed to be easy-to-use for people with different background. If you are a data engineer who is familiar with frameworks born out of Hadoop ecosystem, you can choose to run the whole workflow on Hadoop and Spark Cluster. If you are a data scientist who is used to Python ecosystem, then you can choose to run it on Modin and Ray, where Modin is for distributed data preprocessing and Ray for distributed XGboost training. But if you want to use Spark for data preprocessing and Ray for training or Modin for data preprocessing and Spark for training, it is also possible with the workflow.
The T4 workflow contains extensive data processing & feature engineering techniques. The image below gives an overview of the major data preprocessing steps for stage-1 training.
Regarding stage-2, the only difference is that stage-2 data preprocessing includes one more feature engineering technique called Count Encoding and it also split data into train and validation sets.
Clone Recommender System with Classical ML Repository.
git clone https://github.com/intel/recommender-system-with-classical-ml
cd recommender-system-with-classical-ml
git checkout mlops-release
To download the challenge dataset, please follow the instructions on the official website of RecSys2021 Challenge. We are not allowed to transfer the challenge dataset or host it publicly on the web.
| Type: | Format | Size | Shape |
|---|---|---|---|
| Training Dataset | 201 parquet files | 231 GiB (1.2 GiB each) | (63565312, 25) |
| Validation Dataset | 1 csv file | 6.8 GiB | (17354112, 25) |
To make it easier for users to test the workflow, we include a python script to make synthetic data, which is under the path src/data_loader. You can use the following command to generate synthetic data:
(Optional) Export related proxy into docker environment.
export DOCKER_RUN_ENVS="-e ftp_proxy=${ftp_proxy} \
-e FTP_PROXY=${FTP_PROXY} -e http_proxy=${http_proxy} \
-e HTTP_PROXY=${HTTP_PROXY} -e https_proxy=${https_proxy} \
-e HTTPS_PROXY=${HTTPS_PROXY} -e no_proxy=${no_proxy} \
-e NO_PROXY=${NO_PROXY} -e socks_proxy=${socks_proxy} \
-e SOCKS_PROXY=${SOCKS_PROXY}"export DATASET_DIR=<Path to Dataset>
docker run \
$DOCKER_RUN_ENVS \
--volume ${DATASET_DIR}:/mnt/data \
--volume $(pwd):/mnt \
--privileged --init -it --rm \
--workdir=/mnt \
intel/ai-workflows:analytics-with-python \
/bin/bash -c 'python3 src/data_loader/generate_data.py --save_path /mnt/data'Below setup and how-to-run sessions are for users who want to use provided docker image.
For bare metal environment, please go to bare metal session.
docker pull intel/ai-workflows:analytics-with-python
To quickly set up a working environment if you are in the single-node & single-container mode, please follow the steps below. For other modes of training and step-by-step directions please follow the Interactive Training section of this guide.
(Optional) Export related proxy into docker environment.
export DOCKER_RUN_ENVS="-e ftp_proxy=${ftp_proxy} \
-e FTP_PROXY=${FTP_PROXY} -e http_proxy=${http_proxy} \
-e HTTP_PROXY=${HTTP_PROXY} -e https_proxy=${https_proxy} \
-e HTTPS_PROXY=${HTTPS_PROXY} -e no_proxy=${no_proxy} \
-e NO_PROXY=${NO_PROXY} -e socks_proxy=${socks_proxy} \
-e SOCKS_PROXY=${SOCKS_PROXY}"To run the pipeline, follow below instructions outside of docker instance.
if ! docker network inspect hadoop
then
docker network create --driver=bridge hadoop
fi
export OUTPUT_DIR=/output
export DATASET_DIR=<Path to Dataset>
docker run \
-a stdout $DOCKER_RUN_ENVS \
--net=hadoop \
-p 8088:8088 \
-p 8888:8888 \
-p 8080:8080 \
-p 9870:9870 \
-p 9864:9864 \
-p 4040:4040 \
-p 18081:18081 \
-p 12345:12345 \
--name hadoop-master \
--hostname hadoop-master \
--volume ${OUTPUT_DIR}:${OUTPUT_DIR} \
--volume /${DATASET_DIR}:/mnt/data \
--volume $(pwd)/tmp:/mnt \
--volume $(pwd)/analytics-with-python/config:/mnt/config \
--volume $(pwd):/mnt/code \
--privileged --init -it --rm \
--workdir=/mnt/code \
intel/ai-workflows:analytics-with-python \
/bin/bash -c \
"service ssh start && \
/mnt/code/run-all.sh" $ make recsys-challenge
./analytics-with-python/hadoop-folder-prep.sh .
-e
remove path if already exists....
-e
create folder for hadoop....
if ! docker network inspect hadoop ; then \
docker network create --driver=bridge hadoop; \
fi
[]
[+] Building 0.9s (13/13) FINISHED
=> [internal] load build definition from Dockerfile 0.0s
=> => transferring dockerfile: 2.32kB 0.0s
=> [internal] load .dockerignore 0.0s
=> => transferring context: 2B 0.0s
=> [internal] load metadata for docker.io/library/python:3.7-buster 0.8s
=> [auth] library/python:pull token for registry-1.docker.io 0.0s
=> [1/8] FROM docker.io/library/python:3.7-buster@sha256:2703aeb7b87e849ad2d4cdf25e1b21cf575ca1d2e1442a36f24017a481578222 0.0s
=> CACHED [2/8] RUN DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get -y update && DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get -y install --no-install-recommends openssh-server ssh wget vim net-tools git ht 0.0s
=> CACHED [3/8] RUN wget --no-check-certificate https://repo.huaweicloud.com/java/jdk/8u201-b09/jdk-8u201-linux-x64.tar.gz && tar -zxvf jdk-8u201-linux-x64.tar.gz && mv jdk1.8.0_201 /opt 0.0s
=> CACHED [4/8] RUN wget --no-check-certificate https://dlcdn.apache.org/hadoop/common/hadoop-3.3.3/hadoop-3.3.3.tar.gz && tar -zxvf hadoop-3.3.3.tar.gz && mv hadoop-3.3.3 /opt/hadoop-3. 0.0s
=> CACHED [5/8] RUN wget --no-check-certificate https://dlcdn.apache.org/spark/spark-3.3.0/spark-3.3.0-bin-hadoop3.tgz && tar -zxvf spark-3.3.0-bin-hadoop3.tgz && mv spark-3.3.0-bin-hado 0.0s
=> CACHED [6/8] RUN wget --no-check-certificate http://distfiles.macports.org/scala2.12/scala-2.12.12.tgz && tar -zxvf scala-2.12.12.tgz && mv scala-2.12.12 /opt/scala-2.12.12 && rm 0.0s
=> CACHED [7/8] RUN ssh-keygen -t rsa -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa -P '' && cat /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> /root/.ssh/authorized_keys && sed -i 's/# Port 22/Port 12345/' /etc/ssh/ssh_config && 0.0s
=> CACHED [8/8] RUN pip install --no-cache-dir pyarrow findspark numpy pandas transformers torch pyrecdp sklearn xgboost 0.0s
=> exporting to image 0.0s
=> => exporting layers 0.0s
=> => writing image sha256:a76c8bf585a22bfffe825988f7cf6213bc8b737895694a0f55a7661f4805ffb9 0.0s
=> => naming to docker.io/library/recsys-challenge:training-python-3.7-buster 0.0s
Use 'docker scan' to run Snyk tests against images to find vulnerabilities and learn how to fix them
[+] Running 1/0
⠿ Container hadoop-master Recreated 0.1s
Attaching to hadoop-master
hadoop-master |
hadoop-master | prepare spark dev environment....
hadoop-master |
hadoop-master | format namenode...
...
hadoop-master | #########################
hadoop-master | ### retweet_timestamp
hadoop-master | #########################
hadoop-master | Training.....
hadoop-master | [0] train-logloss:0.62301 valid-logloss:0.62302
hadoop-master | [25] train-logloss:0.24346 valid-logloss:0.24299
hadoop-master | [50] train-logloss:0.23107 valid-logloss:0.23059
hadoop-master | [75] train-logloss:0.22883 valid-logloss:0.22877
hadoop-master | [100] train-logloss:0.22766 valid-logloss:0.22803
hadoop-master | [125] train-logloss:0.22674 valid-logloss:0.22753
hadoop-master | [150] train-logloss:0.22602 valid-logloss:0.22720
hadoop-master | [175] train-logloss:0.22534 valid-logloss:0.22693
hadoop-master | [200] train-logloss:0.22477 valid-logloss:0.22675
hadoop-master | [225] train-logloss:0.22422 valid-logloss:0.22658
hadoop-master | [249] train-logloss:0.22381 valid-logloss:0.22648
hadoop-master | Predicting...
hadoop-master | took 228.5 seconds
hadoop-master | #########################
hadoop-master | ### retweet_with_comment_timestamp
hadoop-master | #########################
hadoop-master | Training.....
hadoop-master | [0] train-logloss:0.60022 valid-logloss:0.60020
hadoop-master | [25] train-logloss:0.05844 valid-logloss:0.05846
hadoop-master | [50] train-logloss:0.03246 valid-logloss:0.03270
hadoop-master | [75] train-logloss:0.03087 valid-logloss:0.03150
hadoop-master | [100] train-logloss:0.03037 valid-logloss:0.03133
hadoop-master | [125] train-logloss:0.03002 valid-logloss:0.03127
hadoop-master | [150] train-logloss:0.02971 valid-logloss:0.03125
hadoop-master | [175] train-logloss:0.02948 valid-logloss:0.03124
hadoop-master | [200] train-logloss:0.02923 valid-logloss:0.03123
hadoop-master | [219] train-logloss:0.02906 valid-logloss:0.03123
hadoop-master | Predicting...
hadoop-master | took 201.8 seconds
hadoop-master | #########################
hadoop-master | ### like_timestamp
hadoop-master | #########################
hadoop-master | Training.....
hadoop-master | [0] train-logloss:0.67215 valid-logloss:0.67171
hadoop-master | [25] train-logloss:0.55620 valid-logloss:0.55312
hadoop-master | [50] train-logloss:0.54695 valid-logloss:0.54384
hadoop-master | [75] train-logloss:0.54348 valid-logloss:0.54068
hadoop-master | [100] train-logloss:0.54142 valid-logloss:0.53901
hadoop-master | [125] train-logloss:0.53950 valid-logloss:0.53753
hadoop-master | [150] train-logloss:0.53816 valid-logloss:0.53661
hadoop-master | [175] train-logloss:0.53689 valid-logloss:0.53576
hadoop-master | [200] train-logloss:0.53588 valid-logloss:0.53516
hadoop-master | [225] train-logloss:0.53500 valid-logloss:0.53470
hadoop-master | [249] train-logloss:0.53422 valid-logloss:0.53431
hadoop-master | Predicting...
hadoop-master | took 230.8 seconds
hadoop-master | reply_timestamp AP:0.13177 RCE:17.21939
hadoop-master | retweet_timestamp AP:0.34489 RCE:19.32879
hadoop-master | retweet_with_comment_timestamp AP:0.02778 RCE:8.86315
hadoop-master | like_timestamp AP:0.70573 RCE:20.61987
hadoop-master | 0.1318 17.2194 0.3449 19.3288 0.0278 8.8631 0.7057 20.6199
hadoop-master | AVG AP: 0.3025420714922875
hadoop-master | AVG RCE: 16.507797035487055
hadoop-master | This notebook took 888.9 seconds
hadoop-master |
hadoop-master |
hadoop-master |
hadoop-master | all training finished!
hadoop-master exited with code 0
sudo rm -rf tmp
| Training Type: |
|---|
| Single-Node & Single-Container Version |
| Multi-Node & Multi-Container Version |
| Usage Mode: |
|---|
| Data Preprocessing |
| Training |
For bare metal environment, please go to Bare Metal Installation Doc
The hardware below is recommended for use with this reference implementation.
- one host machine that has comparable configurations as follows
| Name: | Description |
|---|---|
| CPU | Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8380 CPU @ 2.30GHz (160 vCPUs) |
| Free RAM | 460 GiB/503 GiB |
| Disk Size | 1.5 TB |
| Disk Type | Sata-INTEL_SSDSC2KB019T7_PHYS7412006U1P9DGN |
Note:
It is also possible to run through the code using a machine with a smaller RAM, but then you will need to manually set the spark.driver.memory to a value that your machine can handle in the datapre.py script. But if you have not enough free disk space, Spark/Hadoop will have trouble processing all the raw data. In this case, you can consider reducing the data amount for preprocessing (note: it would affect the prediction accuracy) or use the already processed data to run the training job.
Intel® AI Analytics Toolkit (AI Kit)
Please refer to Hadoop Traps & Pitfalls and Spark Traps & Pitfalls for more information.