- Intro to machine learning
- Reducing Loss
- Training and Testing sets
- Logistic Regression
- First Steps with Tensorflow
Machine learning is the art of making sense of data !
-
It does things normal code can't do and it helps to reduce the time you spend for coding.
-
In machine learning we don't need to tell the algorithm what to do, we only need to show it some examples.
- Supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
In supervised learning we create “models”, a model is basically a function that takes in simple inputs and produces useful predictions. Here we have features and labels in the dataset.
Features:
A feature is an input variable—the x variable in simple linear regression. A simple machine learning project might use a single feature, while a more sophisticated machine learning project could use millions of features.
Features of house price predicting ML model can be,
- Total number of rooms.
- Age of house
- Locality of the house
Labels:
A label is the thing we're predicting. It can be the price of a product, class probability in a classification.
Regression Vs Classification
A regression model is used to predict continuous values.
For example,
- The probability of Captain America Dying in Avengers 4.
- Price of houses in california.
A classification model predicts discrete values. It can make predictions that answer questions like,
- Is this an image of a cat or dog or Wade wilson.
- Pedicting whether a movie belongs to DC or Marvel(based on the dark screen may be)
Linear Regression
Linear regression is a method for finding the straight line or hyperplane that best fits a set of points.
The line equation is,
y = mx + b
In machine learning we use this convention instead,
y' = b + w1x1
Where,
- y' is the label we are predicting.
- b is the bias.
- w1 is the weight of feature 1. Weight is the same concept as the "slope" in the traditional equation of a line.
- x1 is a feature (a known input).
To predict, just substitute the x1 values to the trained model.
A sophisticated model can use more than one features.
y' = b + w1x1 + w2x2 + w3x3 + .... + wNxN
-
Training a model simply means learning (determining) good values for all the weights and the bias from labeled examples.
-
In supervised learning, a machine learning algorithm builds a model by examining many examples and attempting to find a model that minimizes loss; this process is called empirical risk minimization.
-
Loss is the penalty for a bad prediction. If the model's prediction is perfect, the loss is zero; otherwise, the loss is greater.
-
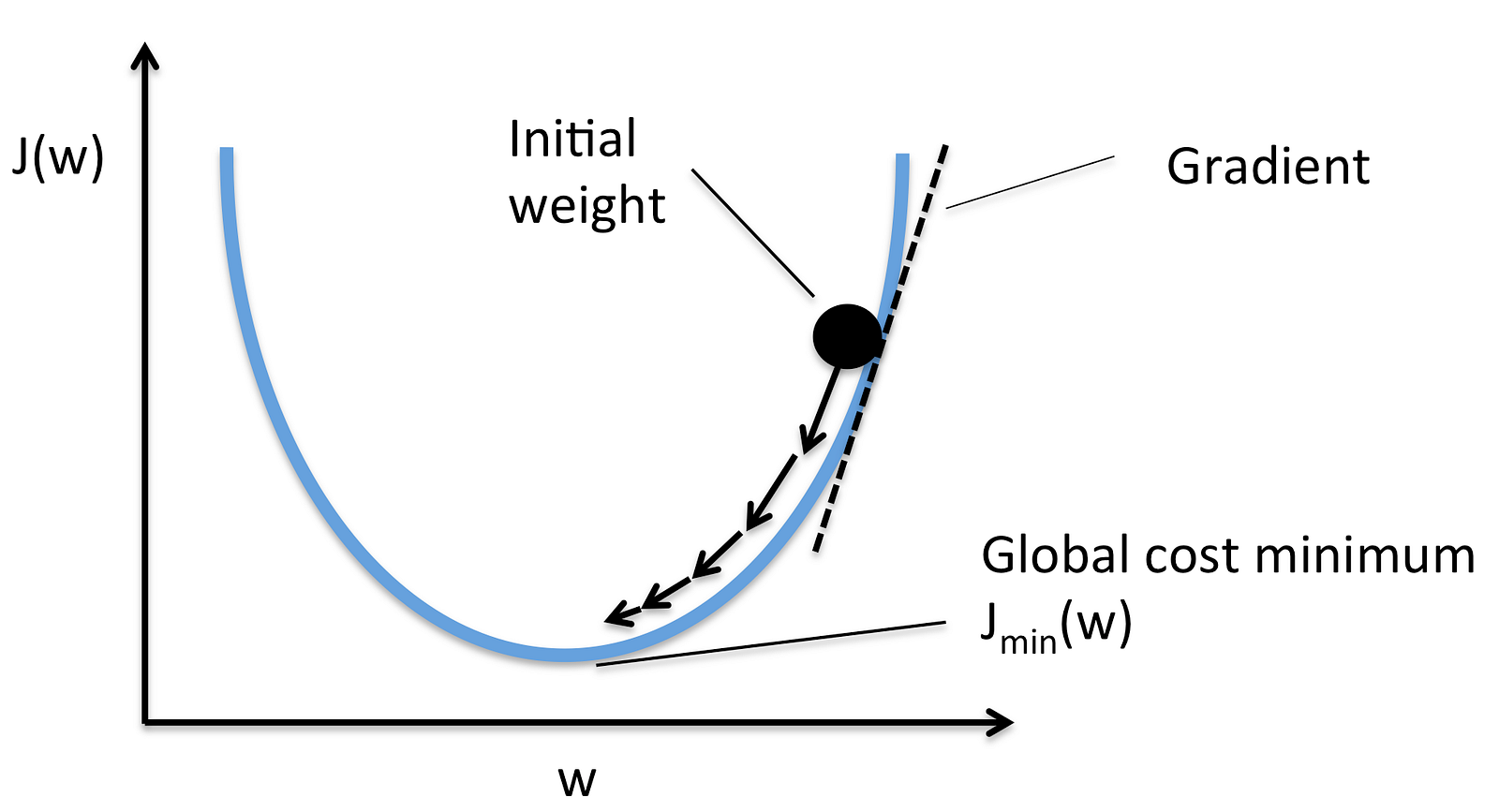
The goal of training a model is to find a set of weights and biases that have low loss, on average, across all examples.
First we have to find the loss.
L2 Loss/square loss is a popular loss function. It is the given as
= the square of the difference between the label and the prediction
= (observation - prediction(x))2
= (y - y')2
Mean square error (MSE) is the average squared loss per example over the whole dataset.
Reducing the loss is similar to the "Hot and cold game" kids play!
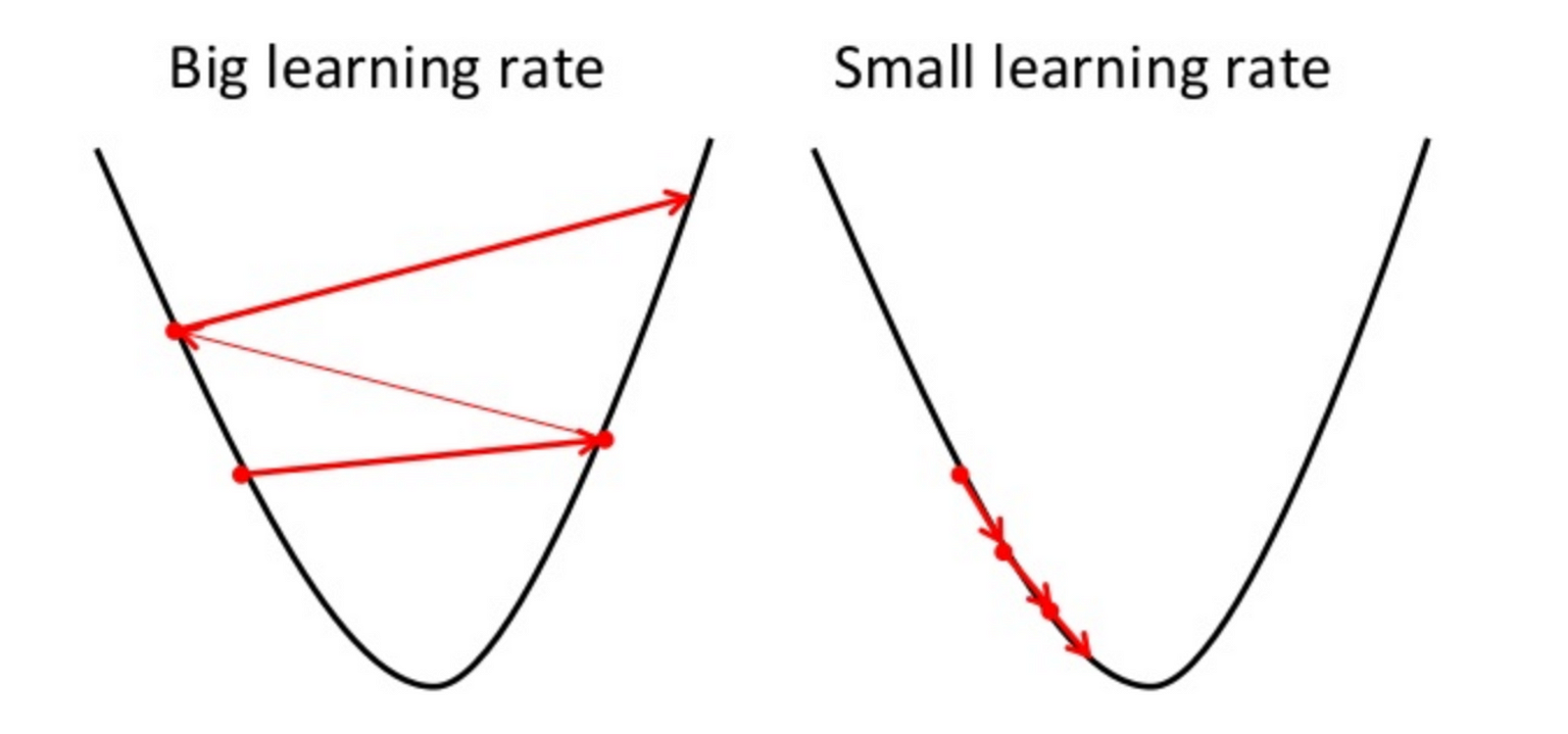
A Machine Learning model is trained by starting with an initial guess for the weights and bias and iteratively adjusting those guesses until learning the weights and bias with the lowest possible loss.
-
Our goal is to create a machine learning model that generalizes well to new data.
-
We train the model using a Training set and the test set act as a proxy for new data!
- training set — a subset to train a model.
- test set — a subset to test the trained model.
- Many problems require a probability estimate as output.
- Logistic regression is an extremely efficient mechanism for calculating probabilities.
P(thenga|day) = 0.05
coconut falling on head =
0.05*365
~= 18
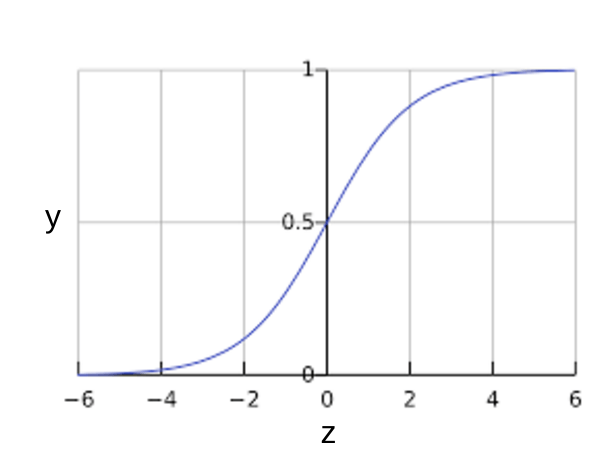
- a sigmoid function, defined as follows, produces output that always falls between 0 and 1.
Where,
y = w1x1 + w2x2 + ... wNxN
and p is the predicted output.
Loss function for Logistic regression is Log Loss
Lets start !